Rare Earth Neodymium-Iron-Boron Permanent Magnet, SH Grade
Rare Earth Neodymium-Iron-Boron Permanent Magnet, SH Grade
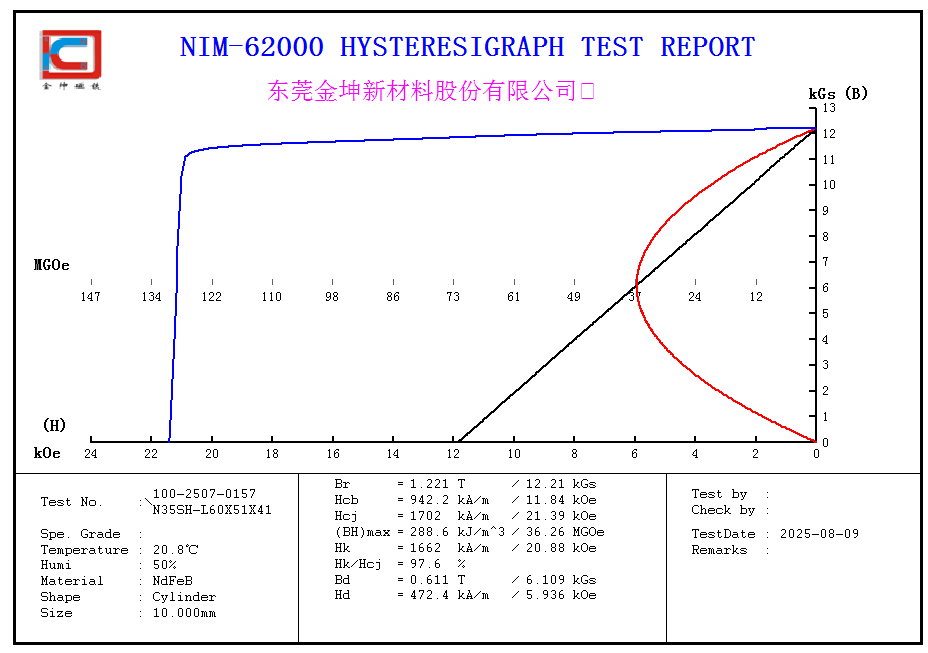
Core Performance Parameters:
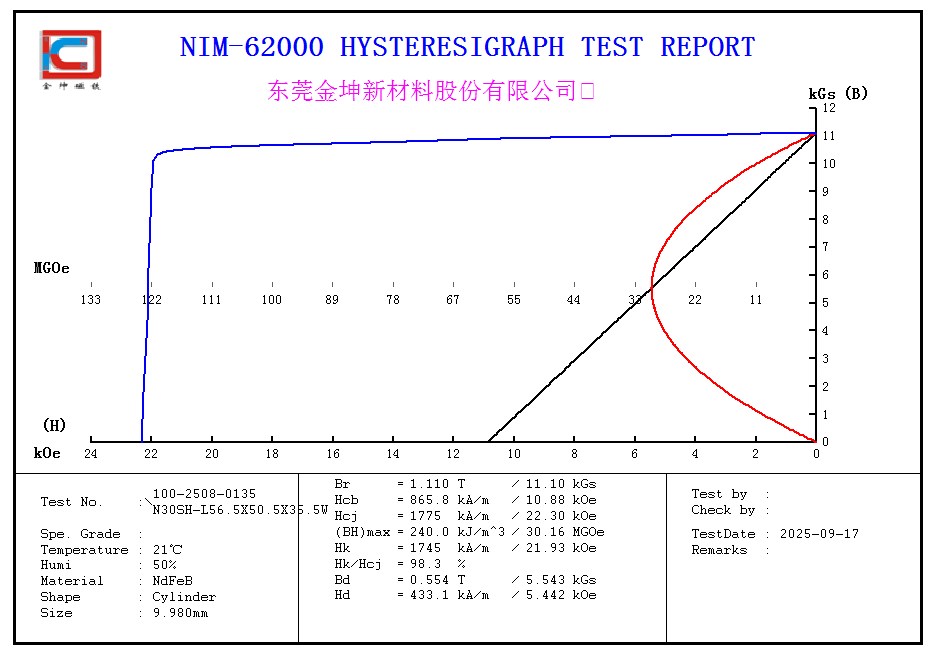
Residual Induction (Br): ~1.1–1.3 T — Maintains excellent magnetic properties, delivering a strong and stable magnetic field.
Intrinsic Coercivity (Hcj): ≥ 18–20 kOe — Significantly enhanced resistance to demagnetization, adaptable to harsher environments.
Maximum Energy Product (BHmax): ~270–360 kJ/m³ — High energy density ensuring strong magnetic effect.
Maximum Operating Temperature: Up to 150 °C — Much higher than N, M, and H grades, suitable for high-temperature environments.
Comparison with Other Grades:
N Grade: Maximum heat resistance 80 °C, limited to low-temperature applications.
M Grade: Heat resistance improved to 100 °C, but restricted to medium-temperature use.
H Grade: Heat resistance ~120 °C, widely adopted in standard industrial applications.
SH Grade: Highest heat resistance (150 °C), retaining stable magnetic performance under high temperatures, though with higher cost.
Comprehensive Advantages:
Outstanding High-Temperature Performance: Capable of continuous operation in environments up to 150 °C.
Stability and Reliability: Very low risk of demagnetization even under high temperature and external interference.
Ideal for High-End Equipment: Meeting the most demanding requirements for temperature and stability in industrial and automotive fields.
Typical Applications & Cases:
Automotive Industry: New energy vehicle drive motors, ABS systems, electric turbochargers — designed to withstand high under-hood temperatures.
Industrial Equipment: High-temperature servo motors, downhole measurement tools, wind power generators — ensuring reliability under elevated temperatures and continuous operation.
Home Appliances & Power Systems: Motors operating in high-heat environments (e.g., dryers, industrial heating equipment).
Medical & Specialized Fields: Certain medical imaging devices and high-precision testing instruments — requiring both high-temperature resistance and long-term stability.




Jinconn WeChat